ONE BIG UNION WINS
By LESLIE H. MARCY and FREDERICK SUMNER BOYD
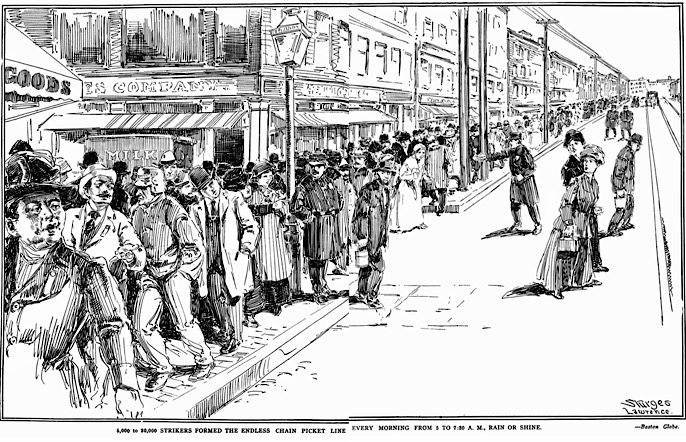

5,000 to 20,000 Strikers Formed the Endless Chain Picket Line
Every Morning from 5 to 7:30 A. M., Rain or Shine.-Boston Globe
Brute force was not, however, the only weapon used by the bosses to try to crush the workers. They had allied with them the A. F. of L., the Catholic church and the Civic Federation a very holy trinity!
Two days after the strike was called John Golden, a member of the Militia of Christ, wired Mayor Scanlon, who had called for militia, asking whether he could be of any assistance to the authorities in suppressing the “rabble,” which he described as anarchistic. Golden and the Lawrence Central Labor Union, affiliated with the A. F. of L., joined in praising the authorities for importing soldiers, and declared that their presence was necessary for “the preservation of order.”
Neither by word nor deed did Golden or the C. L. U. condemn the authorities or their tools for the barbarities and atrocities committed. Vice President Ramsden of the C. L. U., whose two daughters were scabbing in the Arlington mill, when interviewed by the writer was loud in his praises of the militia and the authorities, referred to the I. W. W. as an anarchistic organization that fomented violence and lawlessness, and declared it should be suppressed. He asserted that there was no strike and no organization-only a rabble. When he was asked about the dynamite plot engineered by the bosses through their tool John J. Breen, he naturally refused to comment.
Golden publicly declared that the program of the I. W. W. had acted very much to the advantage of the Textile Workers Union, as it was bringing the latter in closer touch with the mill owners, who understood that it would be more to their interests to deal with the organization, he, Golden, represented rather than with the revolutionary and uncompromising I. W. W.
After having wired, proffering his assistance to the chief of police, Golden got busy in other directions. The mule spinners, numbering according to their own officials, some 180 men, were the only body organized in Lawrence that was affiliated with the A. F. of L. Golden’s union did not have a single member in the whole city. Nevertheless he, in conjunction with Joe R. Menzie, president of the C. L. U., issued circulars to all C. L. U. bodies asking for funds to aid the strike and expressly asking them not to send assistance to the I. W. W.
Then the C. L. U. opened a separate fund. So, too, did Father Melasino, and a man by the name of Shepherd appeared on the scene with some sort of free lunch counter, also appealing for funds.
These various appeals for financial assistance, all made in the name of the strikers of Lawrence, and all calculated to injure the I. W. W. succeeded in diverting large sums of money, the C. L. U. benefiting largely at the expense of the I. W. W. Several times committees from the I. W. W. went to the C. L. U. with evidence that money had been misdirected, but restitution was invariably refused.
Here it may be said that in the seventh week of the strike the C. L. U. strike relief station was practically suspended, applicants being told that the strike was off and that they should return to the mills.
Golden’s next move was to endeavor to organize rival labor unions based on the many crafts in the mills. For several days strenuous attempts were made to divide the workers in the old, old way. Meetings were called by Golden and Menzie, a great deal of money was spent on so-called organizing which had been contributed to the relief funds, and every effort was made to break the solidarity of the workers and get them to return piecemeal.
These efforts failed, the only result being that when the bosses made an offer of five per cent increase over the cut rates—equivalent to an increase of one and one-eighth per cent—a handfull of double-dyed scabs whom Golden had secured to do his work went into the mills.
Golden has shown himself in this fight in his true light, and all the world knows him for a traitor to the working class, and his craft unions are a thing of the past. What Golden did was merely in accord with the policy and doings of the official A. F. of L., and many of the rank and file of the Federation have already woke up to the game of their alleged leaders.
The Ironmolders’ Union that was affiliated with the Lawrence C. L. U. denounced in a resolution the doings of Golden and his gang and withdrew their affiliation. A motion denouncing Golden and his tactics was lost in the Boston Central Labor Union by a vote of 18 to 16. The Central Federated Union of New York City, one of the slimiest haunts of the professional labor crooks in America, even passed a resolution virtually telling Golden to keep his hands off. The Philadelphia Textile Workers’ Union, which had received the Golden appeal, reprinted the I. W. W. appeal for funds and sent several thousand dollars to the I. W. W. war chest.
The latest development in Philadelphia is that 2,000 textile workers have requested I. W. W. organizers to go there and organize a local. All over the country local A. F. of L. unions have denounced Golden and his official friends, and the rank and file of the A. F. of L. has gone on record solidly in favor of their class and against their officials.
Continue reading “Hellraisers Journal: International Socialist Review: One Big Union Wins Great Victory at Lawrence, Massachusetts, Part III” →
 —————
—————

 —————
—————
 —————
—————
 —————
—————
 —————
—————
 —————
————— —–
—–

 —————
—————
 And in Wales it was my good fortune to be there, not to theorize but to take part in the general strike among the coal miners. Previous to my coming, or in previous strikes, the Welsh miners had been in the habit of quitting work, carrying out their tools, permitting the mine managers to run the pumps, allowing the engine winders to remain at work, carrying food down to the horses, keeping the mines in good shape, while the miners themselves were marching from place to place singing their oldtime songs, gathering on the meeting grounds of the ancient Druids and listening to the speeches of the labor leaders; starving for weeks contentedly, and on all occasions acting most peaceably; going back to work when they were compelled to by starvation.
And in Wales it was my good fortune to be there, not to theorize but to take part in the general strike among the coal miners. Previous to my coming, or in previous strikes, the Welsh miners had been in the habit of quitting work, carrying out their tools, permitting the mine managers to run the pumps, allowing the engine winders to remain at work, carrying food down to the horses, keeping the mines in good shape, while the miners themselves were marching from place to place singing their oldtime songs, gathering on the meeting grounds of the ancient Druids and listening to the speeches of the labor leaders; starving for weeks contentedly, and on all occasions acting most peaceably; going back to work when they were compelled to by starvation. ———-
———-
 ———-
———-
